Why Qualified Electronic Signatures are the Most Secure Type of eSignatures?
Electronic Identification, Authentication, and Trust Services (eIDAS) is the EU regulation on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the European Union Market. It defines 3 types of electronic signatures, simple electronic signatures, advanced electronic signatures, and qualified electronic signatures, each having distinct levels of evidential power and legality to approve or execute a document transaction.
The fundamental distinction between the diverse types of signatures is based on the security standards, compliance, encryption techniques, and regulations that establish the legal structure for electronic identification, signatures, tamper-proof seals, and documents throughout under the law of the land. Read on for detailed information on types of signatures, their working, and their distinction from each other.
Electronic Signatures (SES)
This is an electronic form of a signature that includes a scanned signature image or a click of an “I accept” button. Using this type of signature, a signer can provide evidence of their acceptance or approval of a document along with a trusted timestamp. With MSB Docs, anyone can sign the document using this type of signature without getting registered or validating their identity.
Advanced Electronic Signatures (ADES)
This type of electronic signature is mostly referred to as digital signatures and provides the highest level of trust and assurance while accepting or approving a document. These signatures must meet specific requirements to become legally admissible, including signer ID verification, security key, and tamper-proofing. Each user has a unique signing key that ensures ease of validation, remote signing, and non-repudiation.
Electronic Signatures (QES)
The level of trust and assurance that QES holds is one step ahead of the AES type of signatures. QES has a special legal status in the EU member state, and these signatures are considered equivalently legal to a hand-written signature. In addition to the user’s signing key, a formal registration process is also followed by the user to perform a stringent signer verification. This process is carried out by a qualified signature Certificate Authority. A certificate is then issued by any of the trust service providers listed on the EU Trusted List (ETL) and certified by an EU member state.
Difference between Simple Electronic Signatures, Advanced Electronic Signatures, and Qualified Electronic Signatures:
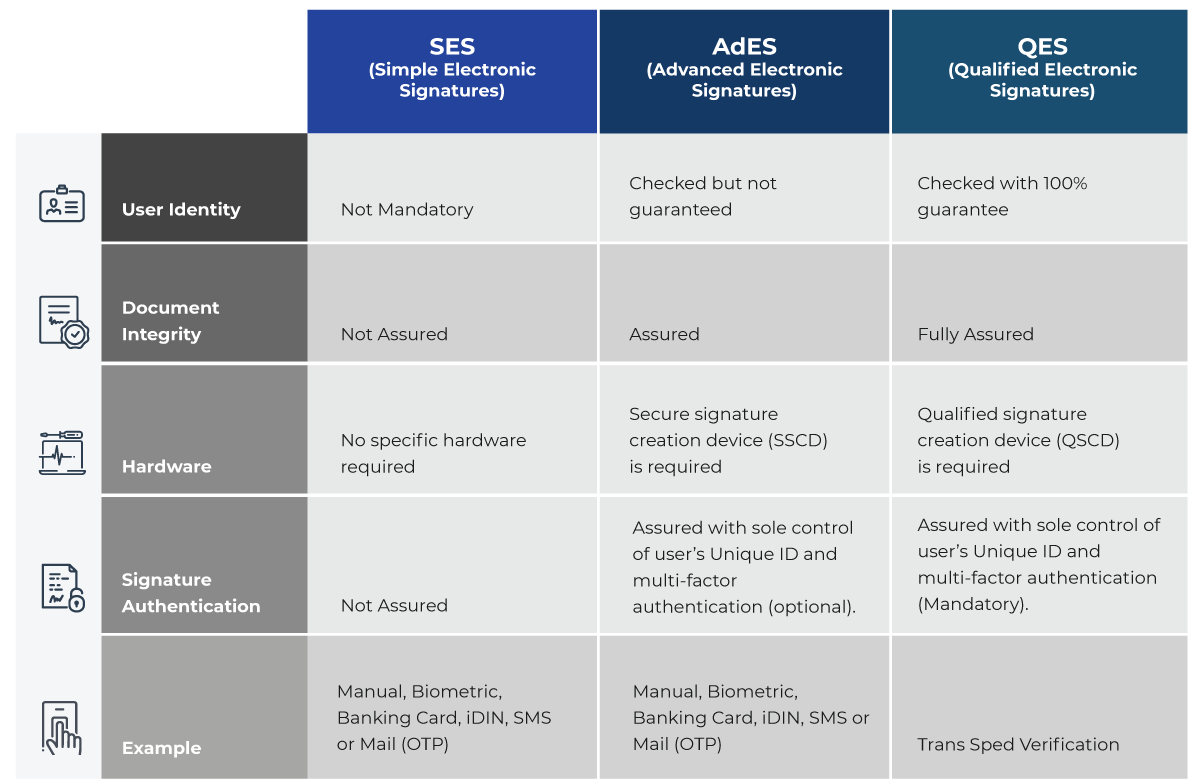
Top 4 Qualified Electronic Signatures Provider
MSB Docs
MSB provides Qualified Signatures valid under EU Electronic Signature regulation eIDAS certified by Trans Sped. Qualified Signatures are required for some documentation under eIDAS, especially with regard to the EMA (European Medicines Agency). Clients from Life Sciences (Pharmaceutical, CRO) industry who are located in or doing business in the European Union is using Trans Ped to sign the documents. The client company requests MSB to issue digital certificates to Signers. Upon which, MSB provides the Subscriber Agreement form to Signers to collect their identification information for their identity. Upon filling and signing the agreement and providing government-issued ID, MSB Trans Sped Trusted Agent schedules a video call with each Signer for identification verification. Once done, Certificate is issued to signers in 48 hours using which documents can be signed anytime anywhere.
DocuSign
To serve EU clients, DocuSign offers all types of signatures that are defined under the eIDAS Regulation, which includes EU Advanced and EU Qualified electronic signatures. These Standards-Based Signatures were initiated as a part of DocuSign’s “Invest for Europe” initiative. This helps in empowering European organizations to automate and manage entire digital document workflows using DocuSign.
DocuSign provides a choice of native and third-party identity management services for identity assurance using DocuSign’s Trust Service Provider Partner (“TSP”) Program. DocuSign has collaborated with multiple providers in the EU, including IBM Intesa, Firmaprofesional, Athens Exchange, IDNow, QuickSign, Swisscom, and others. With the help of these TSPs, electronic ID verification becomes easier and Docusign can provide a complete range of eIDAS-defined signature types.
HelloSign
HelloSign offers the most secure form of eSignatures under eIDAS, i.e., Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) using IDNow (a German-based company that has set the highest standard for online ID verification). Upon selecting “Enable Qualified eSignature”, QES requirements are automatically added to the signature request. Before signing, the signer must verify his or her identity with IDnow. During the verification process, a new window will open and direct the signer to IDnow for a video call with IDNow trusted agent to validate his or her identity. This video verification process is a primary reason QES holds the same legal weightage as in-person signing.
SignRequest
In order to fulfill the eIDAS requirements and offer QES to EU clients, SignRequest adds a ‘signing log’ after each document has been signed. The SignRequest ‘signing log’ includes the following personal information of the signatory:
- Email Address
- All Inputs Made, For Example, Name, Date And Signature
- Ip Address During The Signing
- Time And Date Of The Signature
- Hash Code Of The Signed Document
- Bank Account And Phone Numbers
The signatory can be identified based on the above means which is then attached with a hash code. Any alterations in the signing documents get easily detected and traced. Thus, making QES safe and secure with SignRequest.
Each of the QES providers uses one or the other way to meet eIDAS requirements for identity verification and proof of consent. To reinforce the legal validity of the signatures, collaborate with any one of them.





